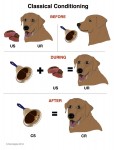
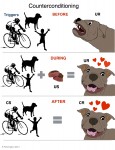
For ethical reasons, we follow a Humane Hierarchy. Dogs learn in two main ways; they learn by consequence and they learn by association. Classical Conditioning employs associative learning. During the 1890’s, Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov’s research using dogs famously led to the discovery of the principles of Classical Conditioning. CC- Classical Conditioning, ( sometimes called Respondant or Pavlovian Conditioning), is a type of learning in which a behavior (conditioned response) comes to be elicited by a stimulus (conditioned stimulus) that has acquired its power through an association with a biologically significant stimulus (unconditioned stimulus). US– Unconditioned Stimulus UR– Unconditioned Response CS– Conditioned Stimulus CR– Conditioned Response CC-Counterconditioning – (yes this is also abbreviated CC) the replacement of an undesirable or maladaptive response to a stimulus with a more desirable response, by means of conditioning procedures +CER- Positive Emotional Response DESENSITIZATION DS- Desensitization is a technique usually paired with counterconditioning, in which the animal is kept below threshold and exposed to fears in an increasing hierarchy of intensity Threshold– The threshold for DS/CC is the point at which your dog is fine, and can calmly take treats while noticing the trigger B.F. Skinner Dogs learn mainly in two ways; they learn by consequence and they learn by association. Operant Conditioning is a type of learning in which an animal modifies behavior based on consequences. B.F. Skinner coined the term Operant Conditioning in 1938 to refer to his theory of how animals learn. OC: Operant Conditioning Behavior: consists of a three-part contingency Antecedent-Behavior- Consequence, or ABC. The antecedent is what happens right before the behavior. The behavior is what the dog does, and the consequence is what happens right after the behavior. Reinforcement: The application or removal of something to increase the occurrence of a behavior Punishment: The application or removal of something to decrease the occurrence of a behavior Reinforcer: something the dog is motivated to acquire (used in R+ and P-) Aversive: Something the dog is motivated to avoid (used in P+ and R-) Differential Reinforcement of an Incompatible behavior (DRI): Reinforcing a desirable behavior which is incompatible with the undesirable behavior. For example, reinforcing your dog with a bit of chicken for sitting and making eye contact with you instead of barking at another dog. In Operant Conditioning, behavior falls into four quadrants: Positive Reinforcement (R+): when a consequence is added which causes behavior to increase. For example, reinforcing your dog with a treat for walking by your side. Heeling increases. Negative Reinforcement (R-): When an aversive that is already present is removed, which causes behavior to increase. In Negative Reinforcement the dog is either trying to escape or avoid. For example, the dog walks by the handler’s side in order to avoid a harsh leash correction on a prong collar, or to escape a continual shock from a shock collar until he moves back into position. Heeling increases. Positive Punishment (P+): when an aversive is added during or right after a behavior, which causes behavior to decrease. For example, a dog is barking and growling at a stranger, and handler grabs dog by the scruff and shakes him. Barking decreases. Negative Punishment (P-): when a rewarding thing is removed which cause a behavior to decrease. For example, the dog is pulling on leash and the handler stops and stands still until the dog stops pulling. The forward motion the dog enjoyed was removed. Pulling decreases. Note: if behavior increases, it’s Reinforcement; if behavior decreases, it’s Punishment. The positive and negative modifiers indicate whether something was added or taken away. Note: The CARE Protocol recommends only R+ Humane Hierarchy
 The use of aversives is neither necessary, nor most humane. For this reason, and for the purpose of behavior change with the CARE protocol, we use only the R+ quadrant of Operant Conditioning to reinforce alternate or incompatible behaviors in conjunction with Desensitization and Counterconditioning.
The use of aversives is neither necessary, nor most humane. For this reason, and for the purpose of behavior change with the CARE protocol, we use only the R+ quadrant of Operant Conditioning to reinforce alternate or incompatible behaviors in conjunction with Desensitization and Counterconditioning.Classical Conditioning
Classical Conditioning: A Practical Guide
CER– Conditioned Emotional ResponseOperant Conditioning

Operant Conditioning: A Practical Guide