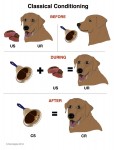
Dogs learn in two main ways; they learn by consequence and they learn by association. Classical Conditioning employs associative learning. During the 1890’s, Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov’s research using dogs famously led to the discovery of the principles of Classical Conditioning.
Classical Conditioning: A Practical Guide
CC- Classical Conditioning, ( sometimes called Respondant or Pavlovian Conditioning), is a type of learning in which a behavior (conditioned response) comes to be elicited by a stimulus (conditioned stimulus) that has acquired its power through an association with a biologically significant stimulus (unconditioned stimulus).
US– Unconditioned Stimulus
UR– Unconditioned Response
CS– Conditioned Stimulus
CR– Conditioned Response
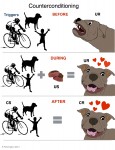
CC-Counterconditioning – (yes this is also abbreviated CC) the replacement of an undesirable or maladaptive response to a stimulus with a more desirable response, by means of conditioning procedures
CER– Conditioned Emotional Response
+CER- Positive Emotional Response
DESENSITIZATION
DS- Desensitization is a technique usually paired with counterconditioning, in which the animal is kept below threshold and exposed to fears in an increasing hierarchy of intensity
Threshold– The threshold for DS/CC is the point at which your dog is fine, and can calmly take treats while noticing the trigger